When Was Glass Introduced to China?
The origin of glass can be traced back to around 5000 BC, and the earliest glassware were found in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia. Around 2000 BC, glass making technology was introduced to ancient Greece and Rome, and developed rapidly.By ancient Rome, stained glass made by the Romans had passed from India to the East.
Glass is often called an "imported product" in China, which shows that people regard this material as foreign, giving it the characteristics and connotation of Western exchanges. The origin of Chinese glass was influenced by Western glass products and production techniques, the most important of which were Western glass beads imported to China through the Silk Road in the late Spring and Autumn Period and early Warring States Period.In ancient books of Qin and Han,the "壁流离" or "流离"(later written as “琉璃(glaze)”) is the early transliteration of Sanskrit glass (spahtika).
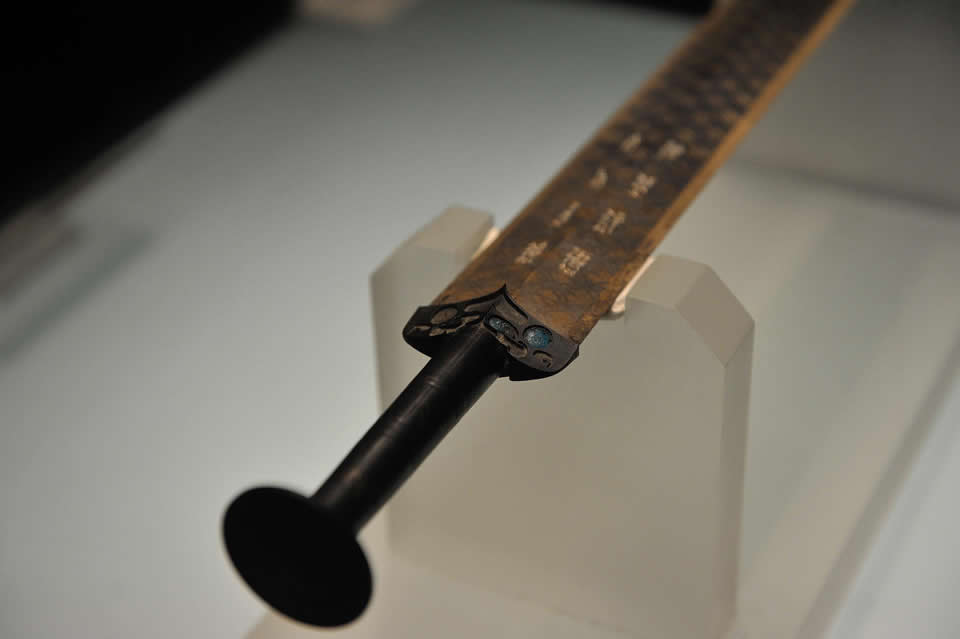

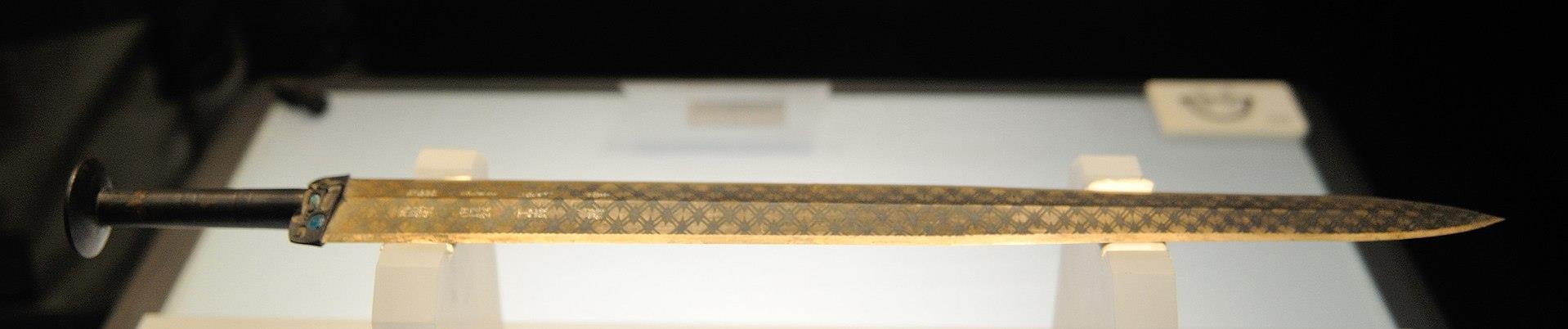
The picture above showed the sword of Goujian,King of Yue(Late Spring and Autumn Period).Its sword grid was inlaid with light blue glass containing many small bubbles on both sides.

The glass plate and glass ear cup unearthed from Liu Sheng's(Prince Jing in Han Dynasty) tomb are the earliest ancient glass vessels discovered by archaeology in China. They were produced by casting method. According to qualitative analysis of the spectrum, their main components are silicon and lead, and contain sodium and barium. They belong to the early Chinese lead Barium glass. The glass disk is emerald green, slightly shiny, and translucent. Partially corroded by soil rust and alkalinization, it appears as milky white spots.
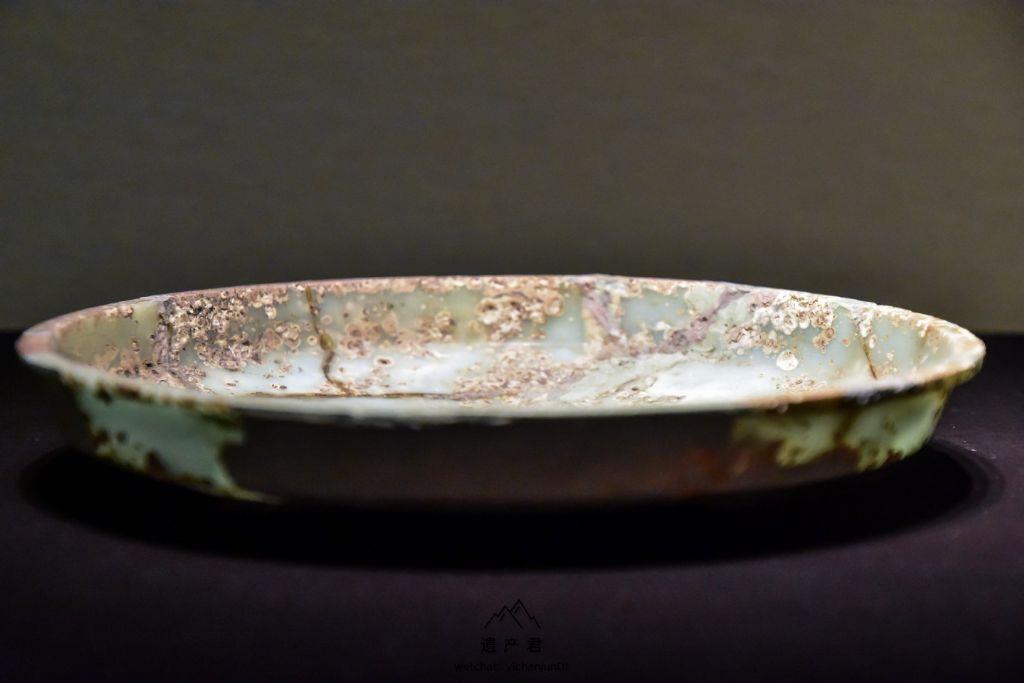

(Glass plate unearthed from the tomb of Liusheng)
At first, the ancients mistakenly believed that colored glaze was the natural treasure.
During the Wei Jin Southern and NOrthern Dynaties,China began to model western glass products,and gradually developed our own glass making process.Although the society was in turmoil, the fighting for wealth and extravagant style of the upper class led to the development of lead-barium glass, and the import of Roman and Sassanian utensils increased. As late as the Northern Wei Dynasty, China had adopted glass blowing technology. Compared with the imported Roman glass and Sasanian glass, the quantity of domestic glassware during this period was relatively small.
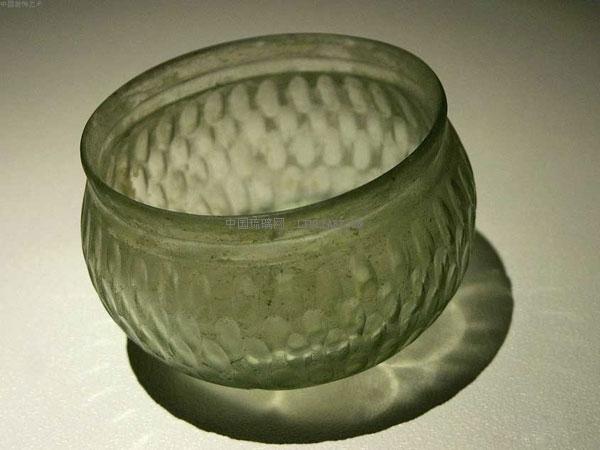

(Light green glass bowl from the Northern Wei Dynasty unearthed in Datong, Shanxi,China - Sasanian)
During the Tang and Song Dynasties, China's glass products manufacturing reached its peak, producing a variety of glassware, such as bowls, cups, bottles, jars, mirrors, etc.
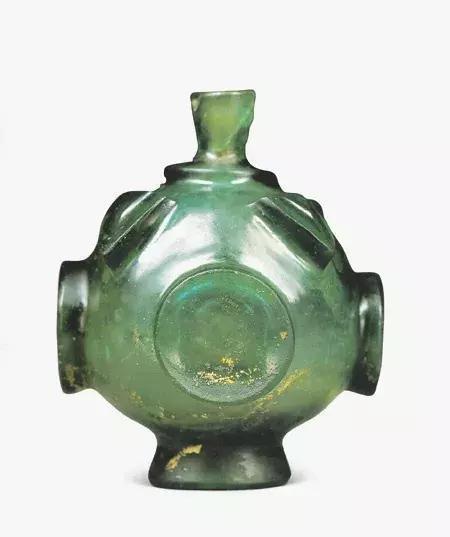
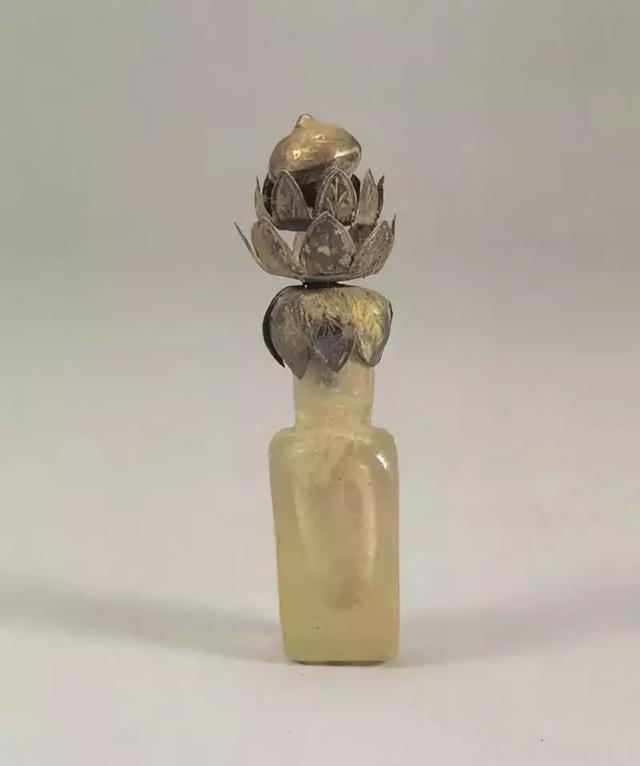


During the Song to Liao dynasties, the high-lead glass craftsmanship of the Tang Dynasty was inherited without significant development. China's glass manufacturing had entered the private sector. It was also from this time that the value of glass began to plummet. Because people's understanding of the material of glass had been clarified, and they knew that it is an artificial material rather than a naturally occurring gemstone.Traditional Chinese glass had not entered the scope of daily life and become a common daily necessities because of its vulnerability,instead ornamental crafts.
Glass was not taken seriously during the Yuan and Ming Dynasties, and even though it was still produced, the technology did not improve much. Due to the maritime ban in the Ming Dynasty, the amount of Western glassware imported into China dropped significantly.This situation did not change until the early Qing Dynasty. The love of glass by the upper class in the Qing Dynasty can be seen. Not only a large amount of European glass was imported into China, but also the Qing Palace Glass Factory was specially established. The popularity of glass was also began in the late Qing Dynasty.
(Blue glass hairpins of women in Song Dynasty)